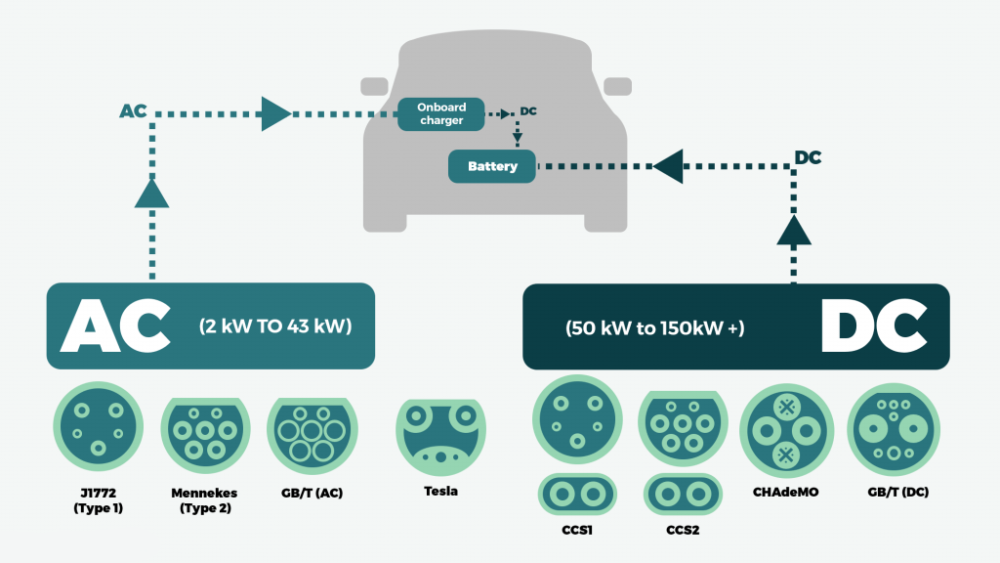
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, understanding the difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) charging is crucial for EV owners. This guide explains these two charging methods in a simple and clear manner, helping you choose the best charging option for your needs.
What is AC Charging?
AC charging is the most common and widely available form of charging for electric vehicles. It is typically used in home and public charging stations.
Key Features of AC Charging:
- Slower Charging Speed: AC charging is slower compared to DC charging, making it ideal for overnight charging at home.
- Lower Cost: AC chargers are generally more affordable to install and use.
- Requires Onboard Charger: The car’s onboard charger converts AC to DC, as EV batteries can only store DC power.
- Common Power Levels: Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) chargers fall under AC charging.
What is DC Charging?
DC charging, also known as fast charging, directly supplies DC power to the EV battery, bypassing the onboard charger.
Key Features of DC Charging:
- Faster Charging Speed: Can charge an EV battery up to 80% in as little as 20-30 minutes.
- Higher Cost: More expensive to install and operate compared to AC chargers.
- Requires High Power Infrastructure: Found mainly at public charging stations and highways.
- Common Power Levels: Ranges from 50 kW to 350 kW, depending on the charger type.
Comparison Table: AC vs. DC Charging
| Feature | AC Charging | DC Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow (4-12 hours) | Fast (20-60 minutes) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Infrastructure | Home & Public | High-Power Public |
| Power Range | 3 kW – 22 kW | 50 kW – 350 kW |
| Usage | Daily, Overnight | Quick Top-Ups |
Charging Speed Comparison
Below is a graphical representation of the time taken to charge an EV with different charger types:
Charging Time for a 60 kWh Battery:
- Level 1 (120V AC): ~40-50 hours
- Level 2 (240V AC): ~4-10 hours
- DC Fast Charger (50 kW): ~1-1.5 hours
- Ultra-Fast DC Charger (150-350 kW): ~20-30 minutes
(Graph Placeholder: A bar chart comparing charging times)
Which One Should You Use?
- For Daily Use: AC charging is sufficient for home or workplace charging.
- For Long Trips: DC fast chargers help reduce charging stops and make travel more convenient.
Recommended Resources
To learn more about AC and DC charging, check out the following resources:
Conclusion
Both AC and DC charging have their advantages and ideal use cases. While AC charging is great for daily home use, DC charging is essential for long-distance travel. Understanding the differences can help EV owners make informed charging decisions and optimize their EV experience.